Identification and Characterization of Novel Factors of Proteostasis and the Autophagy Network
The maintenance of protein homeostasis – a balance between synthesis, folding and controlled degradation of proteins – is of pivotal importance for all cellular functions. Misfolded, damaged, dysfunctional or aggregated proteins basically can be degraded via two different mechanisms: the ubiquitin proteasome system and macroautophagy which encompasses the disassembly of cytoplasmic macromolecules or organelles by means of the lysosomal system. In the course of macroautophagy degradation-prone material is packed into membrane vesicles, so called autophagosomes that are subsequently directed to and fused with lysosomes.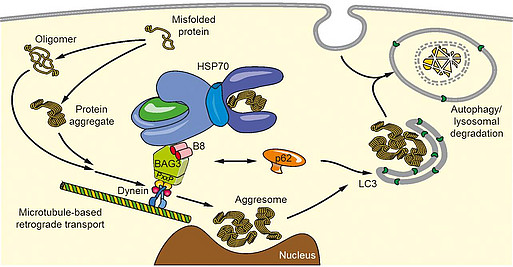
In different model systems we were able to show that cells re-organize their protein degradation mechanisms during aging as well as a response to acute proteotoxic stress and switch from proteasomal to autophagic pathways. This is accomplished by the reciprocal regulation of the co-chaperone proteins BAG1 and BAG3 (BAG1/BAG3-switch). Thus, cells adapt to the oxidative, proteotoxic environment coming along with age by employing BAG3-mediated selective macroautophagy we described for the first time. On a molecular level we were able to identify BAG3 as the factor transferring defective proteins from the chaperone HSP70 identifying those to the motor protein dynein. By that way degradation-prone proteins are transported to the so-called aggresome, a perinuclear structure where they concentrate inside the cell. The kinetics of this process, the regulation of BAG3-mediated selective macroautophagy by post-translational modifications as well as endo- and exogenous factors and, furthermore, the interplay with other autophagy routes we are investigating within the CRC 1177 (project headed by Christian Behl).
Another focus of our research is on the identification of novel factors of proteostasis by using specific C.elegans reporter lines and RNAi libraries. In the course of a RNAi screen we performed we were able to characterize the RAB3GAP complex as a new factor of autophagy that is necessary for the initiation of autophagosomes. RABGAP (RAB GTPases Activating Protein) proteins are components of the cellular vesicle transport system and as regulators of RAB GTPases coordinate different traffic routes. A key challenge of autophagy is to provide the membranes necessary to build up autophagosomes in an adequate extent. In this early step of autophagy the RAB3GAP complex is critically involved, leading to a decrease of autophagic activity if the complex is downregulated and an increase if it is upregulated. As a positive modulator of autophagy the RAB3GAP complex affects protein homeostasis and its dysfunction leads to increased protein aggregation. At present, we work on the specific target structures and the regulation of the complex (project headed by Andreas Kern).
Although a modified regulation of protein homeostasis in the course of cellular aging is described in different model systems it is far from being completely understood. One of the central questions is which factors, e.g. the continuous presence of mutated proteins, account for this modified regulation. Based on the above mentioned RNAi screen in C. elegans we were able to identify RME-8 (mammalian ortholog: DNAJC13) as a factor that impairs the maintenance of protein homeostasis and promotes the aggregation of reporter proteins if it is not present. RME-8, originally described as receptor mediated endocytosis 8, interacts with the retromer complex and participates in several transport processes to and from endosomes. Now, we were able to show that a lack of RME-8 in human cells impairs proteostasis and leads to protein aggregation upon acute cellular stress. In current studies we are analyzing the function of RME-8 as a possible link between the endosomal transport system and the maintenance of protein homeostasis. In cellular aging models as well as primary human fibroblasts from patients suffering from Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis, a deadly motor neuron disease, we are investigating the role of RME-8 in the regulation of proteostasis. Our studies are a project of the CRC 1080 (TP A8 Clement/Behl) and a part of our cooperations within the German Network for Motor Neuron Diseases (MND-NET) (project headed by Albrecht Clement).
A central role of cellular proteostasis is discussed also for acute degenerative processes. In traumatic brain injury (TBI) the degree of functional damage is determined mainly by the expansion of the primary lesion into the surrounding healthy brain tissue. In the vicinity of TBI, in neuronal and glial cells adaptive processes occur to achieve functional reorganization. These need stabilization of protein homeostasis, particularly the degradation of damaged, dysfunctional and aggregated proteins. The objective of a cooperation project between the Institute for Pathobiochemistry, the Department of Anaesthesiology and the Institute for Physiology and Pathophysiology, which is also a project within the CRC 1080 (TP A7 Behl/Engelhard/Mittmann) is to describe the alterations in proteostasis after TBI in detail and to analyze a possible link between reorganization and neuronal survival. For that purpose, a spatial and temporal profile of the different protein degradation pathways is compiled in in vivo models of TBI and correlated with neuronal function monitored by field potential and single cell recordings. First of all, we concentrate on BAG3-mediated selective macroautophagy (project headed by Christian Behl).