Guidelines for collection of patient samples
Blood cultures
- are among the most valuable elements of modern infection diagnostics
- should be correctly removed at the right time
Exudates from closed processes and abscesses
- It is recommended to obtain exudate rich foci by percutaneous puncture and secretion aspiration with a syringe, if they are accessible from outside.
- If processes are to be opened, material should first be obtained by puncture. If this is not successful, abscess contents must be taken up in sufficient quantity by means of a syringe immediately after the incision. In addition, it is recommended to preserve a piece of the granulation tissue of the abscess wall in a separate transport vessel with NaCl.
- In case of little exudate (e.g. skin pustules or bubbles) aspiration with a small syringe (tuberculin syringe)
Exudates from closed processes and abscesses
- In open wounds, secretion is taken with a swab or tissue crumbs from the wound bed and from peripheral districts. Excise small lesions in toto.
- Suction of exudate from fistula ducts using a sterile catheter, if possible, or a curette to remove tissue from the wall of the fistula duct.
CAVE!In chronic inflammatory processes the pathogen concentration is often low, so that a sufficiently large sample volume must be ensured.
Important!
Immediate transport!
Do not store syringes with sealing cone for more than 2 hours (refrigerator)!
Clamydia swabs
Cervix Sample
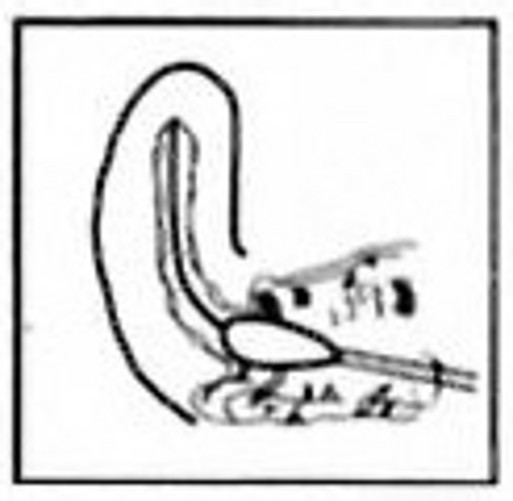
- Remove and discard mucus from the ectocervix with a large swab.
- Insert another large swab into the cervical canal until the tip is no longer visible.
- Turn for 3-5 seconds. Pull out. Avoid touching the vaginal structures.
Urethra samples
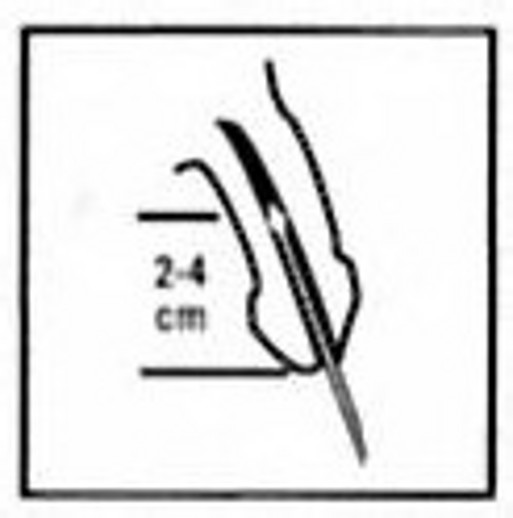
- Do not urinate within one hour prior to specimen collection.
- Insert a small swab 2-4 cm deep into the urethra.
- Rotate back and forth for 3-5 seconds and then pull out.
Sample preparation and transport:
- Immediately after collection, vigorously move the swab back and forth in the STM for 15 seconds. Squeeze liquid against the wall of the tube. Excessive mucus should be absorbed and removed with the swab. Squeeze excess fluid from the mucus on the wall of the tube. If the swab is left in the sample transport medium for more than 15 seconds, this can lead to inhibition of the PCR!
- Remove the swab and excess mucus. Close the tube. Label the sample.
- Transport the sample within 24 hours at 2-25°C.