Generelles zur Microcomputertomographie
Die micro-CT hat sich in den letzten Jahren zu einer in der Forschung fest etablierten Methodik entwickelt. Sie erlaubt es bei höchster räumlicher Auflösung (je nach Gerät und Probe im einstelligen Mikrometerbereich oder sogar im Submikrometerbereich) kleinste Strukturen hochauflösend darzustellen. Bereits mit kurzen Untersuchungszeiten von deutlich unter einer Minute ist die Erstellung hochauflösender Datensätze möglich. Darüber hinaus sind auch Durchleuchtungsuntersuchungen und digitale Subtraktionsangiographien möglich. Da es sich um ein wenig invasives Verfahren handelt, erlaubt die micro-CT auch in der in vivo-Bildgebung die Erfassung longitudinaler Verläufe, was zu einer Reduktion der in Tierversuchen eingesetzten Tierzahlen (3R-Prinzip) bei gleichzeitig besserer Aussagekraft führt.Einsatzbereiche der Micro-CT
Im Detail erlaubt die micro-CT höchstauflösende Untersuchungen ossärer Strukturen (komplettes Skelett, Knochen, Knochenfragmente, Frakturheilung, Zähne etc.) in vitro sowie in vivo. Darüber hinaus können Gefäße sowohl in vivo als CT-Angiographie oder digitale Subtraktionsangiographie als auch ex vivo nach Perfusion mit röntgendichten Polymerisaten hochauflösend abgebildet werden (Angiogenese etc.). Ebenfalls können unterschiedlichste Organe und Gewebe inklusive pathologischer Prozesse ex vivo und in vivo analysiert und differenziert werden (Leber und Lungenmetastasen, entzündliche und sonstige Prozesse der Lunge, Hirntumoren, Knochentumoren, Kolonpolypen, Nieren und Blase, Milz, sowie unterschiedlichste weitere Organsysteme). Im funktionellen Bereich sind Multi-Energy CT, Fettbestimmung, Cardio-CT und weitere Protokolle möglich. Selbstverständlich lassen sich auch Materialien sowie sonstige röntgendichte technische Prüfkörper analysieren.Anfragen zur Nutzung der Kleintier-CT
Sollte Ihr Interesse geweckt worden sein oder sind Sie sich nicht sicher, ob die von Ihnen geplanten Untersuchungen mittels mikro-CT durchgeführt werden können, kontaktieren Sie uns gerne über das Sekretariat der Klinik und Poliklinik für Neuroradiologie. Darüber hinaus verfügen wir neben der micro-CT auch über andere bildgebende Verfahren für größere Objekte und betreiben neben einem micro-CT Deutschlands ersten und bisher einzigen ultrahochauflösenden klinischen Computertomographen (UHR-CT / Aquilion Precision) sowie klinische Kernspintomographen bei 1,5 und 3,0 Tesla Feldstärke.Im Anhang sind einige Bildbeispiele sowie Quellen zu Studien und Kooperationsprojekten rund um die micro-CT aus unserer AG aufgeführt. Für Ihre Fragen stehen wir gerne zur Verfügung.
Publikationen unserer Arbeitsgruppe
- Weyer, V.; Maros, M. E.; Kronfeld, A.; Kirschner, S.; Groden, C.; Sommer, C.; Tanyildizi, Y.; Kramer, M.; Brockmann, M. A., Longitudinal imaging and evaluation of SAH-associated cerebral large artery vasospasm in mice using micro-CT and angiography. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2019, 271678X19887052.
- Henn, D.; Abu-Halima, M.; Wermke, D.; Falkner, F.; Thomas, B.; Kopple, C.; Ludwig, N.; Schulte, M.; Brockmann, M. A.; Kim, Y. J.; Sacks, J. M.; Kneser, U.; Keller, A.; Meese, E.; Schmidt, V. J., MicroRNA-regulated pathways of flow-stimulated angiogenesis and vascular remodeling in vivo. J Transl Med 2019, 17 (1), 22.
- Eweida, A.; Rosenbauer, O.; Frisch, O.; Giordano, F. A.; Fleckenstein, J.; Wenz, F.; Kirschner, S.; Brockmann, M. A.; Schulte, M.; Kneser, U.; Harhaus, L., Irradiation Delays Tissue Growth but Enhances Osteogenic Differentiation in Vascularized Constructs. J Reconstr Microsurg 2019, 35 (1), 46-56.
- Sen, S.; Erber, R.; Kunzmann, K.; Kirschner, S.; Weyer, V.; Schilling, L.; Brockmann, M. A.; Rues, S.; Orhan, G.; Lux, C. J.; Zingler, S., Assessing abrasion of orthodontic surface sealants using a modified ophthalmic optical coherence tomography device. Clin Oral Investig 2018, 22 (9), 3143-3157.
- Neulen, A.; Kosterhon, M.; Pantel, T.; Kirschner, S.; Goetz, H.; Brockmann, M. A.; Kantelhardt, S. R.; Thal, S. C., A Volumetric Method for Quantification of Cerebral Vasospasm in a Murine Model of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. J Vis Exp 2018, (137).
- Eweida, A.; Frisch, O.; Giordano, F. A.; Fleckenstein, J.; Wenz, F.; Brockmann, M. A.; Schulte, M.; Schmidt, V. J.; Kneser, U.; Harhaus, L., Axially vascularized tissue-engineered bone constructs retain their in vivo angiogenic and osteogenic capacity after high-dose irradiation. J Tissue Eng Regen Med 2018, 12 (2), e657-e668.
- Neulen, A.; Pantel, T.; Kosterhon, M.; Kirschner, S.; Brockmann, M. A.; Kantelhardt, S. R.; Giese, A.; Thal, S. C., A segmentation-based volumetric approach to localize and quantify cerebral vasospasm based on tomographic imaging data. PLoS One 2017, 12 (2), e0172010.
- Mackert, G. A.; Schulte, M.; Hirche, C.; Kotsougiani, D.; Vogelpohl, J.; Hoener, B.; Fiebig, T.; Kirschner, S.; Brockmann, M. A.; Lehnhardt, M.; Kneser, U.; Harhaus, L., Low-energy extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) improves metaphyseal fracture healing in an osteoporotic rat model. PLoS One 2017, 12 (12), e0189356.
- Felix, M. C.; Glatting, G.; Giordano, F. A.; Brockmann, M. A.; Wenz, F.; Fleckenstein, J., Collimator optimization for small animal radiation therapy at a micro-CT. Z Med Phys 2017, 27 (1), 56-64.
- Kirschner, S.; Murle, B.; Felix, M.; Arns, A.; Groden, C.; Wenz, F.; Hug, A.; Glatting, G.; Kramer, M.; Giordano, F. A.; Brockmann, M. A., Imaging of Orthotopic Glioblastoma Xenografts in Mice Using a Clinical CT Scanner: Comparison with Micro-CT and Histology. PLoS One 2016, 11 (11), e0165994.
- Kirschner, S.; Felix, M. C.; Hartmann, L.; Bierbaum, M.; Maros, M. E.; Kerl, H. U.; Wenz, F.; Glatting, G.; Kramer, M.; Giordano, F. A.; Brockmann, M. A., In vivo micro-CT imaging of untreated and irradiated orthotopic glioblastoma xenografts in mice: capabilities, limitations and a comparison with bioluminescence imaging. J Neurooncol 2015, 122 (2), 245-54.
- Felix, M. C.; Fleckenstein, J.; Kirschner, S.; Hartmann, L.; Wenz, F.; Brockmann, M. A.; Glatting, G.; Giordano, F. A., Image-Guided Radiotherapy Using a Modified Industrial Micro-CT for Preclinical Applications. PLoS One 2015, 10 (5), e0126246.
- Nittka, S.; Krueger, M. A.; Shively, J. E.; Boll, H.; Brockmann, M. A.; Doyon, F.; Pichler, B. J.; Neumaier, M., Radioimmunoimaging of liver metastases with PET using a 64Cu-labeled CEA antibody in transgenic mice. PLoS One 2014, 9 (9), e106921.
- Keuler, A.; Taschner, C.; Brockmann, M. A.; Boll, H.; Forster, K.; Lutz, L.; Herrmann-Frank, A.; Lelgemann, M.; Schumacher, M., Comparison of high-resolution X-ray and micro-CT for experimental evaluation of intracranial stent prototypes: quality evaluation beyond CE mark. Neuroradiology 2014, 56 (4), 315-23.
- Fiebig, T.; Figueiredo, G.; Boll, H.; Kerl, H. U.; Noelte, I. S.; Forster, A.; Groden, C.; Kramer, M.; Brockmann, M. A., A Low Cost Metal-Free Vascular Access Mini-Port for Artifact Free Imaging and Repeated Injections in Mice. PLoS One 2013, 8 (6), e65939.
- Boll, H.; Figueiredo, G.; Fiebig, T.; Nittka, S.; Doyon, F.; Kerl, H. U.; Nolte, I.; Forster, A.; Kramer, M.; Brockmann, M. A., Comparison of Fenestra LC, ExiTron nano 6000, and ExiTron nano 12000 for micro-CT imaging of liver and spleen in mice. Acad Radiol 2013, 20 (9), 1137-43.
- Figueiredo, G.; Brockmann, C.; Boll, H.; Heilmann, M.; Schambach, S. J.; Fiebig, T.; Kramer, M.; Groden, C.; Brockmann, M. A., Comparison of digital subtraction angiography, micro-computed tomography angiography and magnetic resonance angiography in the assessment of the cerebrovascular system in live mice. Clin Neuroradiol 2012, 22 (1), 21-8.
- Figueiredo, G.; Boll, H.; Kramer, M.; Groden, C.; Brockmann, M. A., In vivo X-ray digital subtraction and CT angiography of the murine cerebrovasculature using an intra-arterial route of contrast injection. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2012, 33 (9), 1702-9.
- Fiebig, T.; Boll, H.; Figueiredo, G.; Kerl, H. U.; Nittka, S.; Groden, C.; Kramer, M.; Brockmann, M. A., Three-dimensional in vivo imaging of the murine liver: a micro-computed tomography-based anatomical study. PLoS One 2012, 7 (2), e31179.
- Kralev, S.; Haag, B.; Spannenberger, J.; Lang, S.; Brockmann, M. A.; Bartling, S.; Marx, A.; Haase, K. K.; Borggrefe, M.; Suselbeck, T., Expansion of the Multi-Link Frontier coronary bifurcation stent: micro-computed tomographic assessment in human autopsy and porcine heart samples. PLoS One 2011, 6 (7), e21778.
- Kerl, H. U.; Isaza, C. T.; Boll, H.; Schambach, S. J.; Nolte, I. S.; Groden, C.; Brockmann, M. A., Evaluation of a continuous-rotation, high-speed scanning protocol for micro-computed tomography. J Comput Assist Tomogr 2011, 35 (4), 517-23.
- Boll, H.; Nittka, S.; Doyon, F.; Neumaier, M.; Marx, A.; Kramer, M.; Groden, C.; Brockmann, M. A., Micro-CT based experimental liver imaging using a nanoparticulate contrast agent: a longitudinal study in mice. PLoS One 2011, 6 (9), e25692.
- Boll, H.; Bag, S.; Nolte, I. S.; Wilhelm, T.; Kramer, M.; Groden, C.; Bocker, U.; Brockmann, M. A., Double-contrast micro-CT colonoscopy in live mice. Int J Colorectal Dis 2011, 26 (6), 721-7.
- Schambach, S. J.; Bag, S.; Schilling, L.; Groden, C.; Brockmann, M. A., Application of micro-CT in small animal imaging. Methods 2010, 50 (1), 2-13.
- Schambach, S. J.; Bag, S.; Groden, C.; Schilling, L.; Brockmann, M. A., Vascular imaging in small rodents using micro-CT. Methods 2010, 50 (1), 26-35.
- Brockmann, M. A., Guest Editor's Introduction: In vivo small-animal imaging using micro-CT. Methods 2010, 50 (1), 1.
- Boll, H.; Bag, S.; Schambach, S. J.; Doyon, F.; Nittka, S.; Kramer, M.; Groden, C.; Brockmann, M. A., High-speed single-breath-hold micro-computed tomography of thoracic and abdominal structures in mice using a simplified method for intubation. J Comput Assist Tomogr 2010, 34 (5), 783-90.
- Bag, S.; Schambach, S. J.; Boll, H.; Schilling, L.; Groden, C.; Brockmann, M. A., [Current concepts for experimental micro-CT in small animals]. Rofo 2010, 182 (5), 390-403.
- Schambach, S. J.; Bag, S.; Steil, V.; Isaza, C.; Schilling, L.; Groden, C.; Brockmann, M. A., Ultrafast high-resolution in vivo volume-CTA of mice cerebral vessels. Stroke 2009, 40 (4), 1444-50.
Forschungsprojekte u. Beispielbilder mit Einsatz von Kleintiertomographie
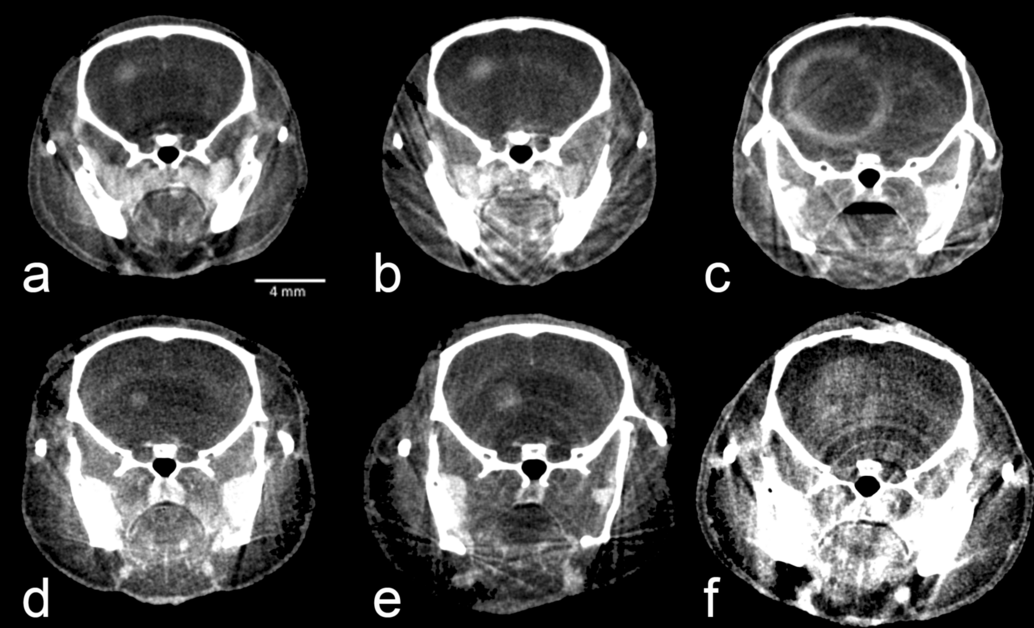
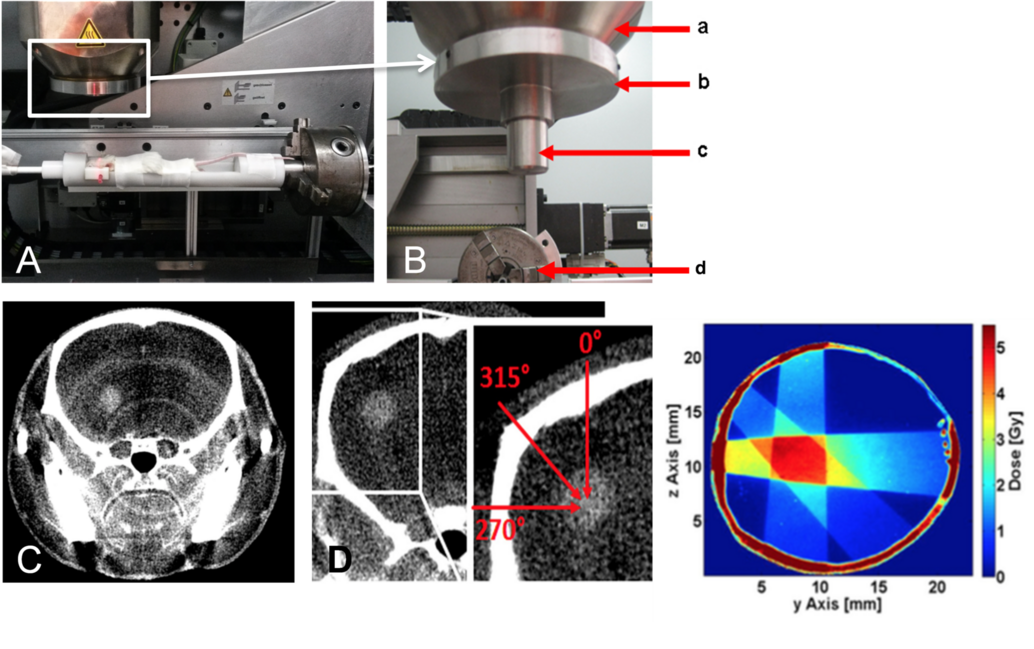
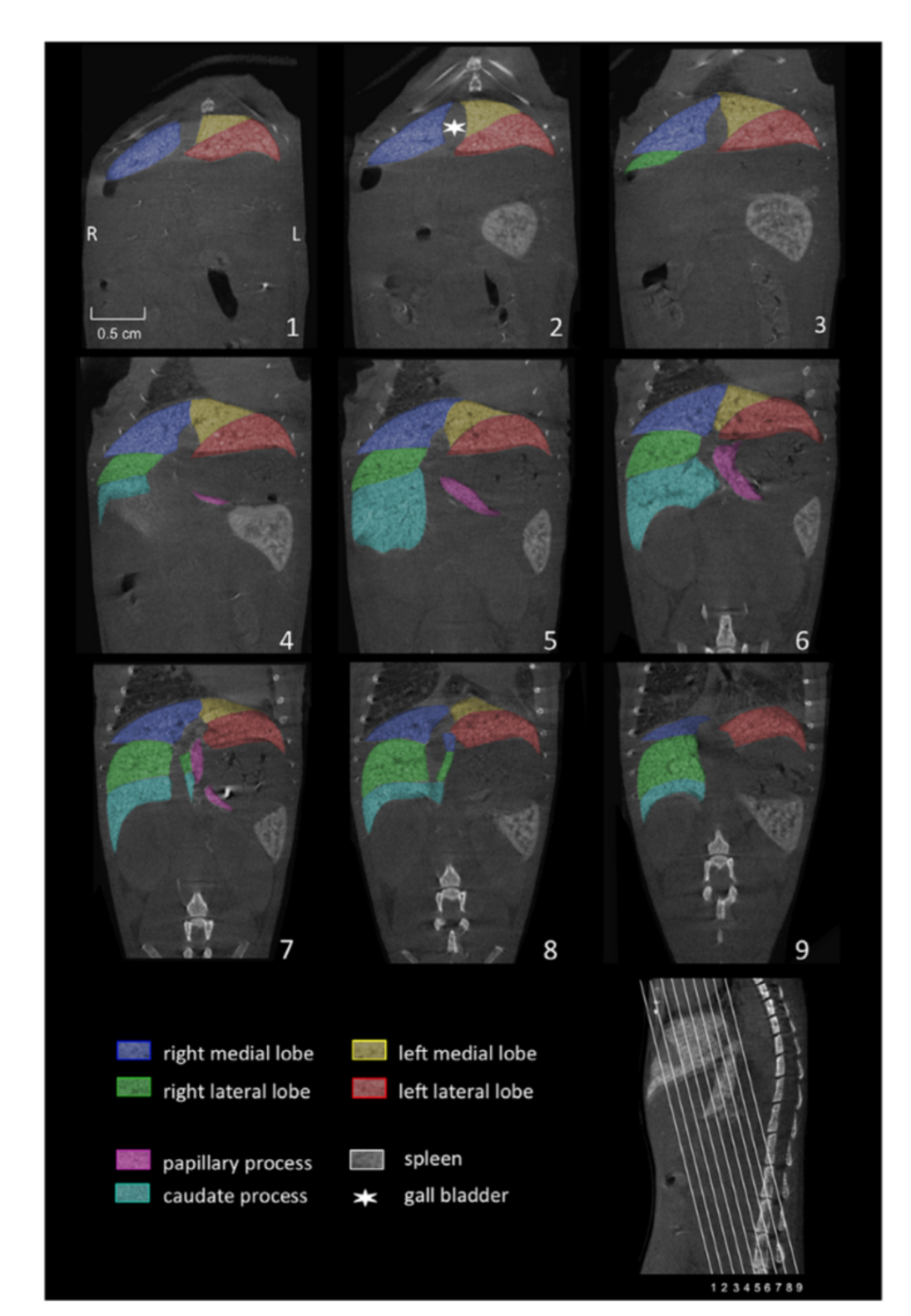
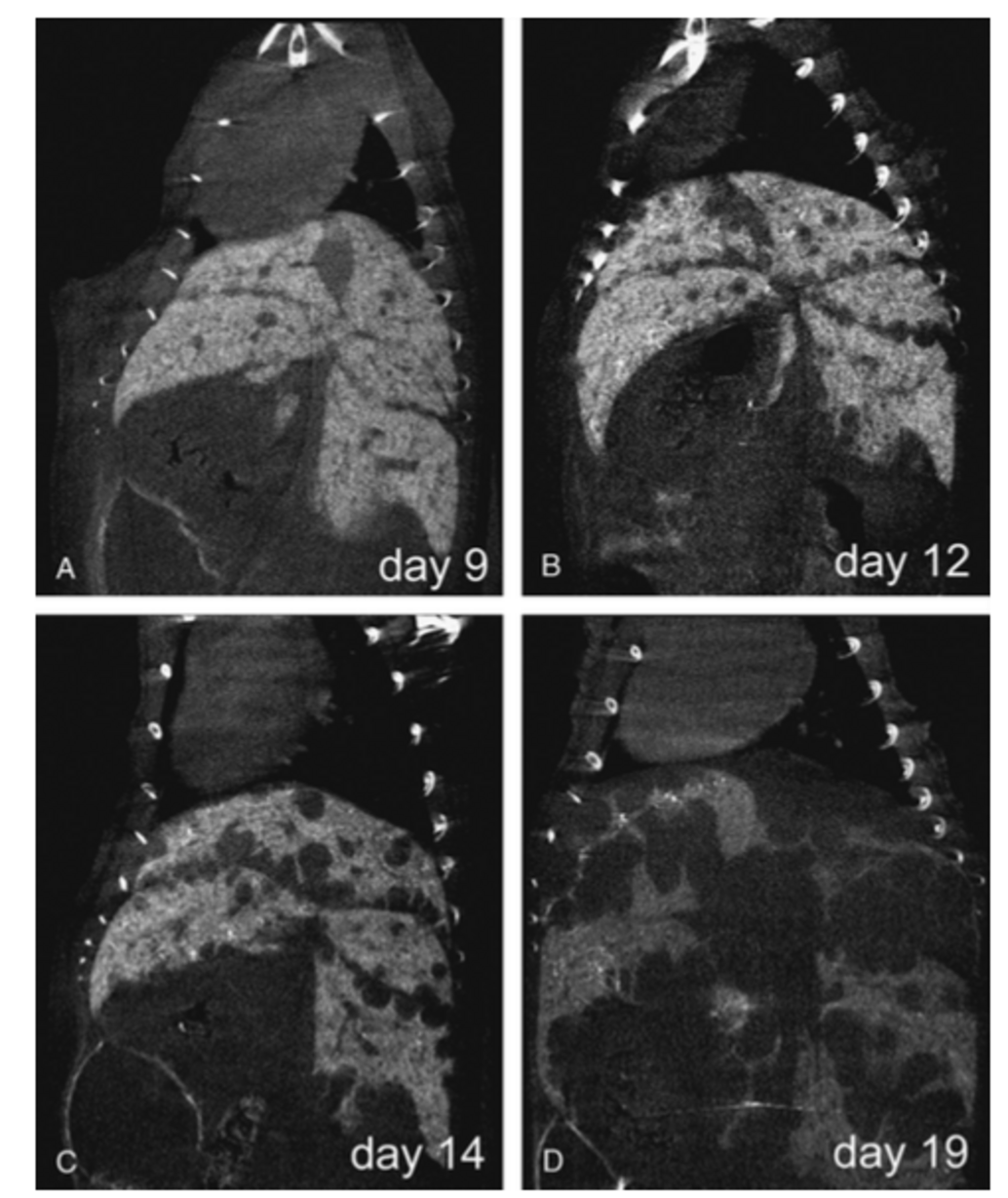
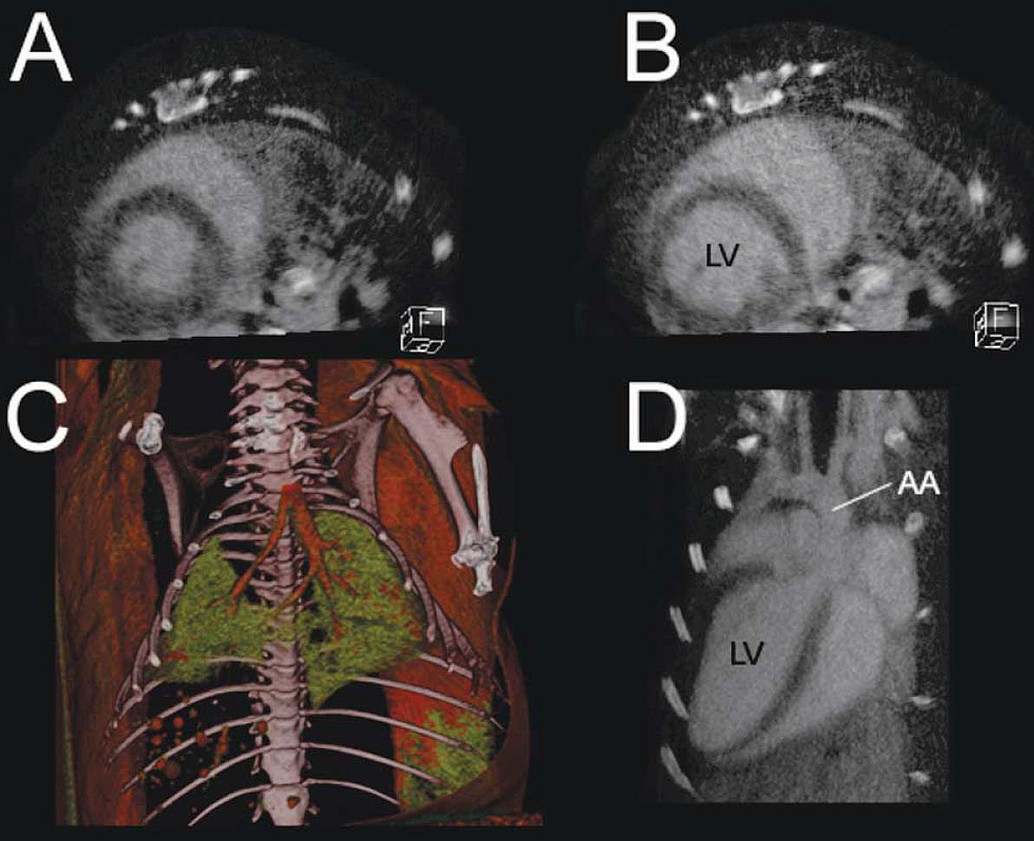
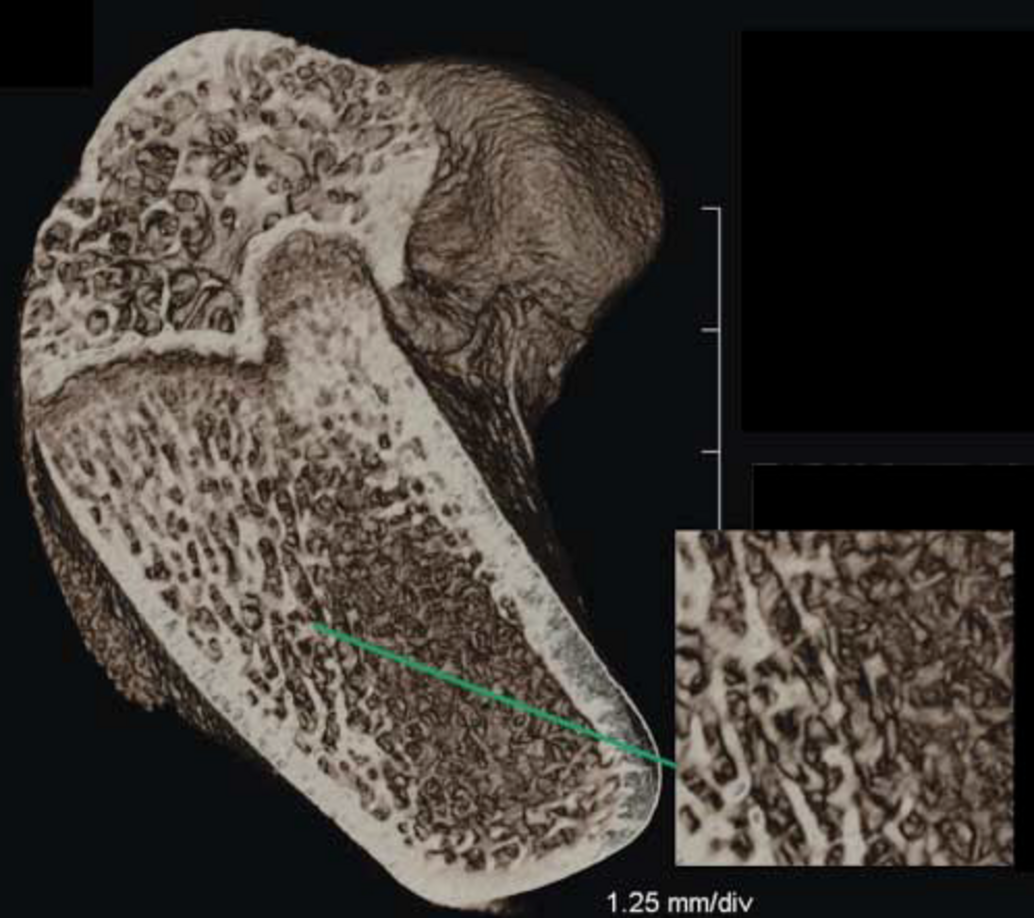
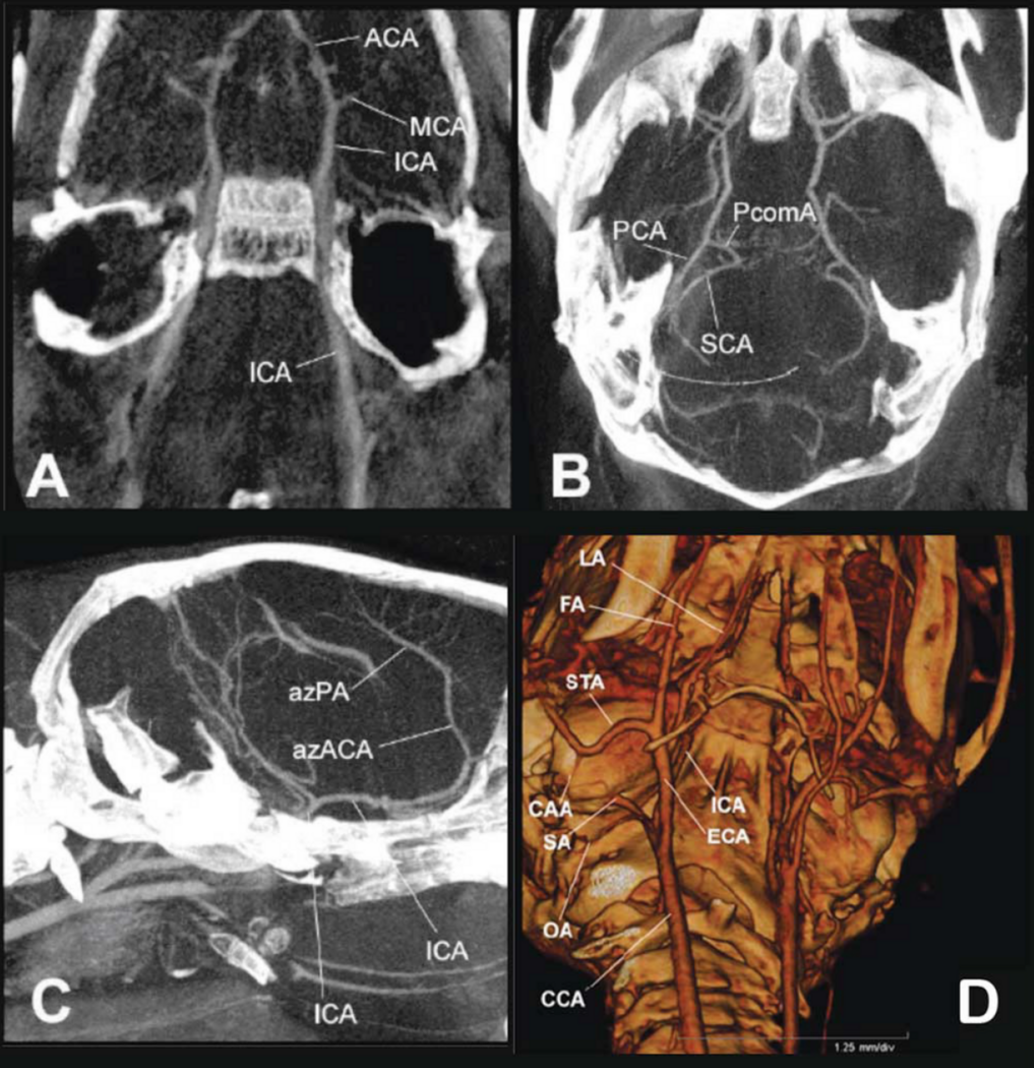
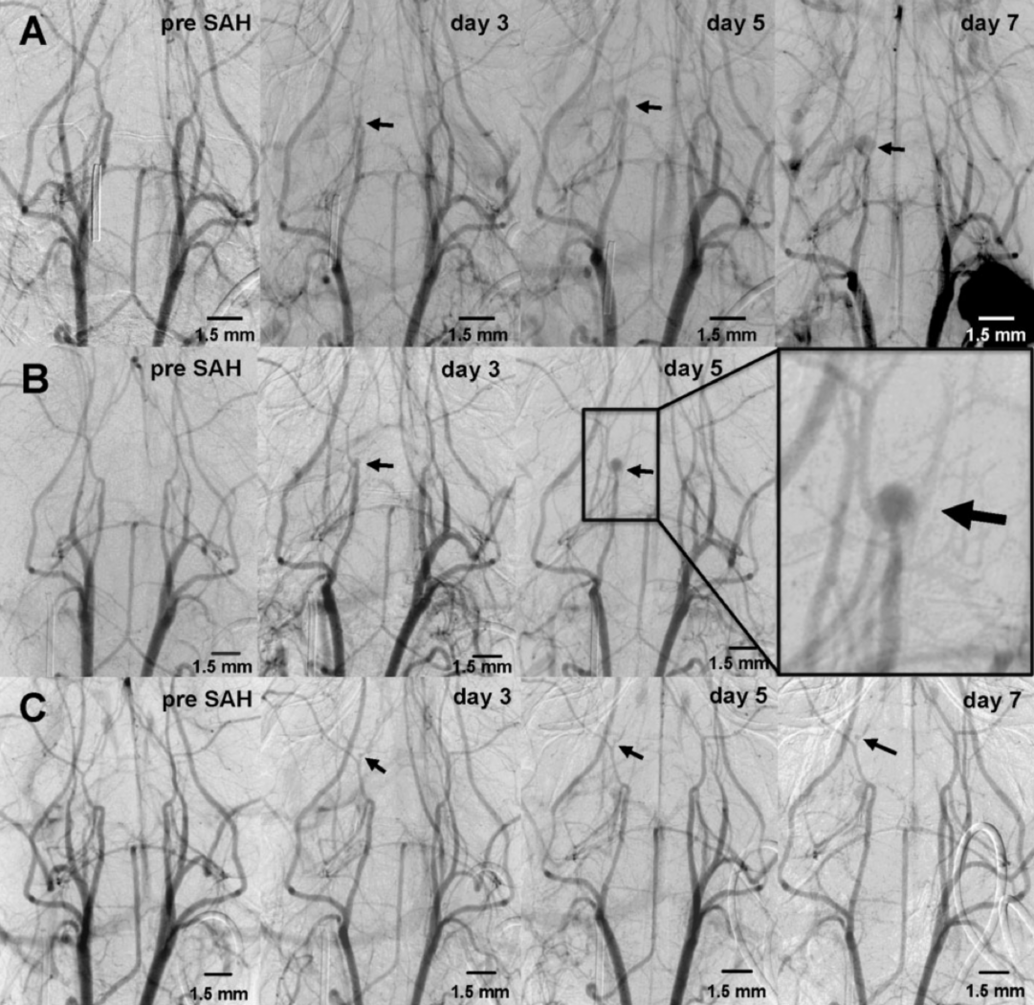
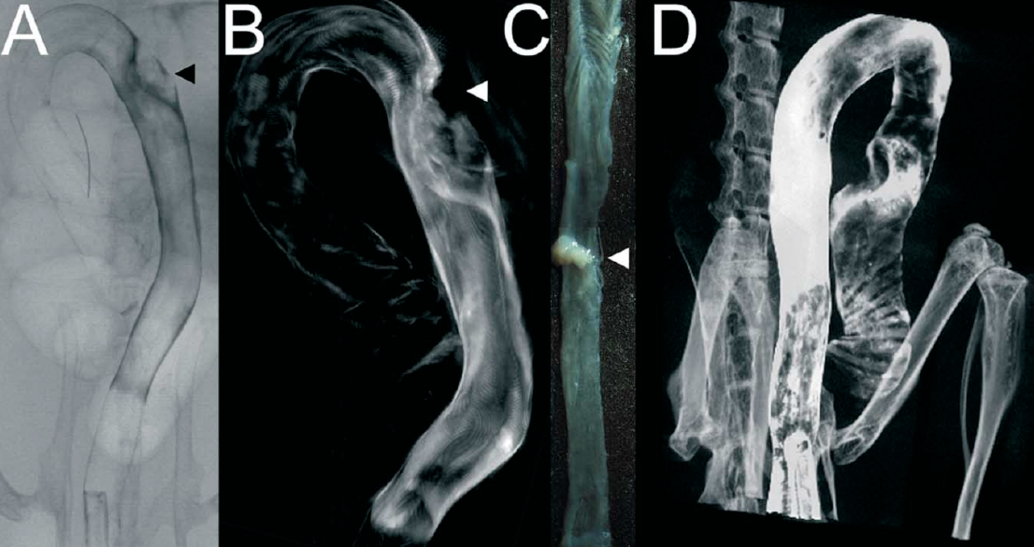

Rekonstruktion von CT-Bildern mit Hilfe der Software Cera (Firma Siemens)
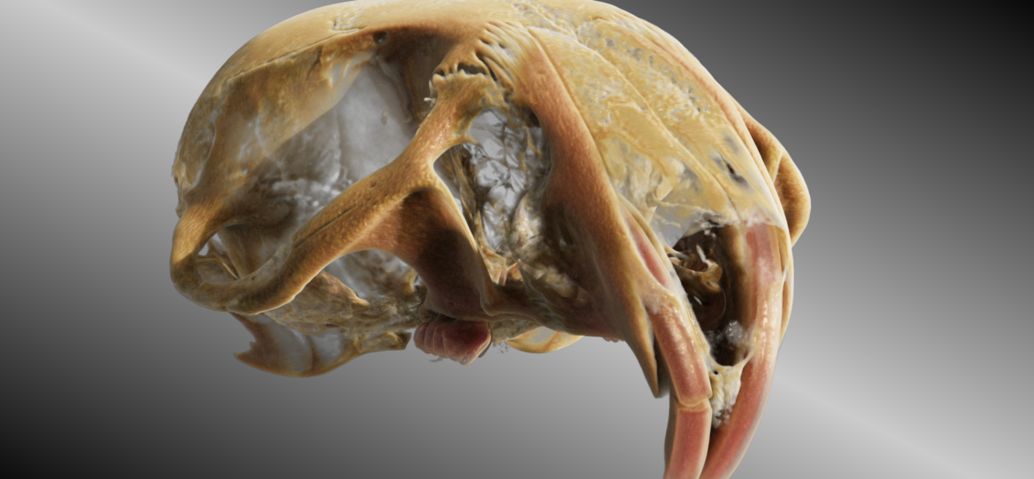
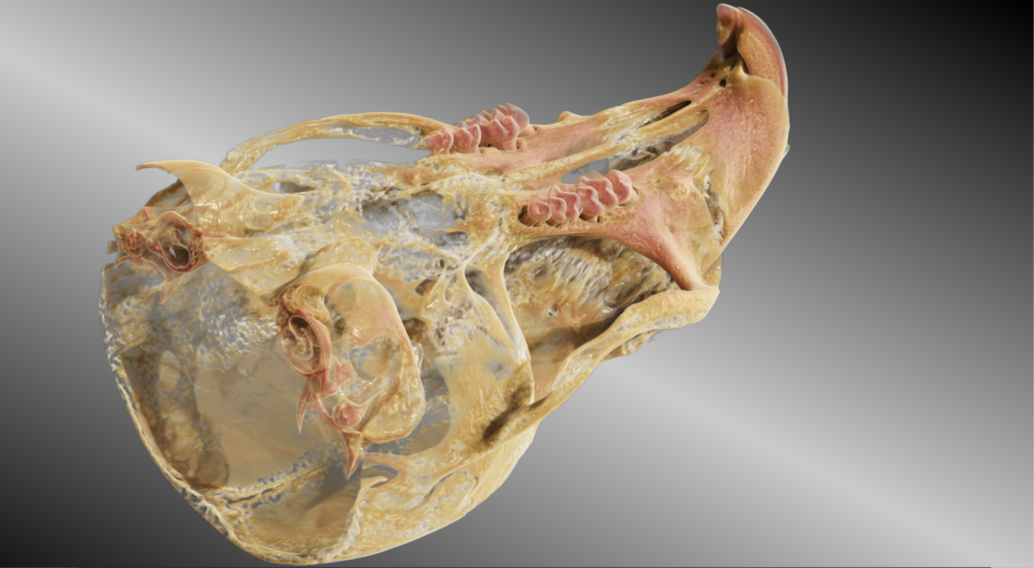
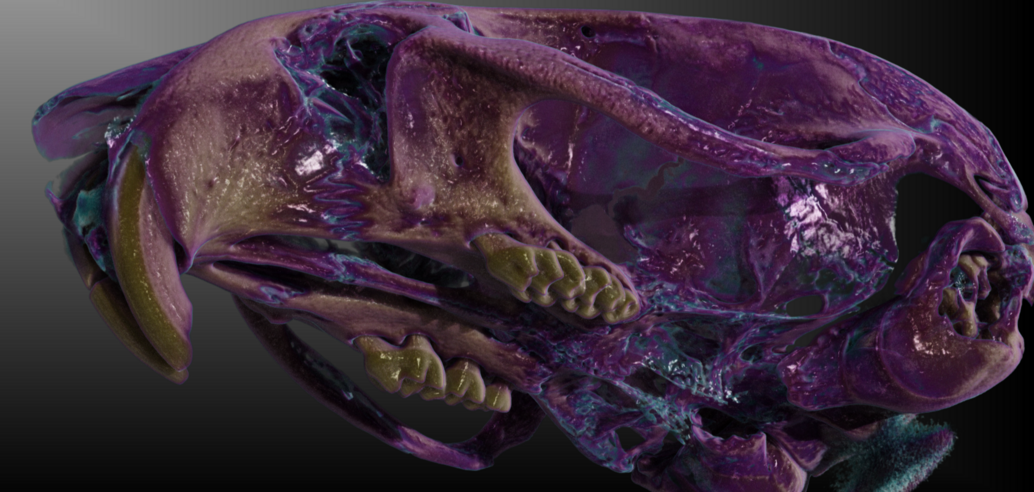
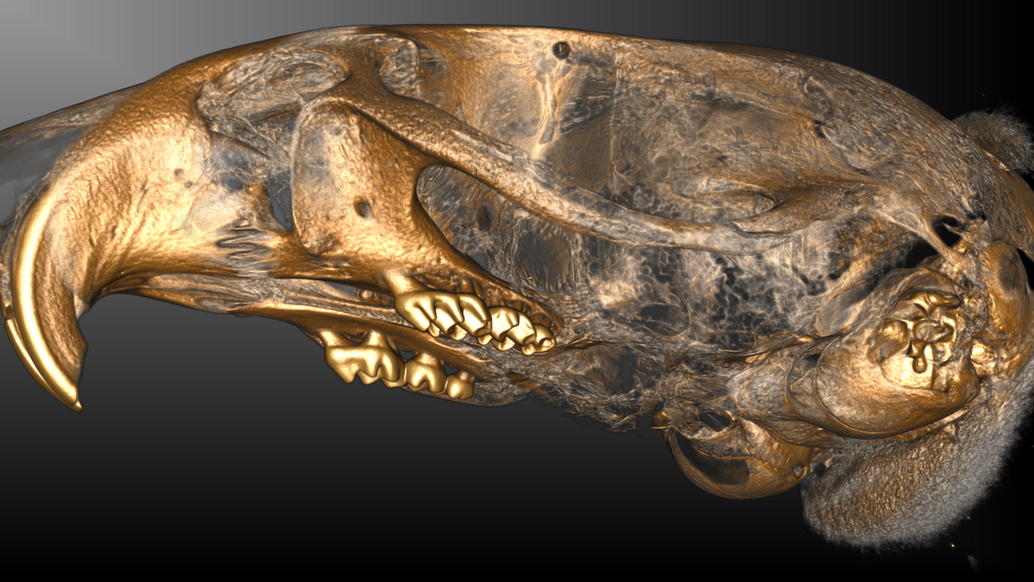
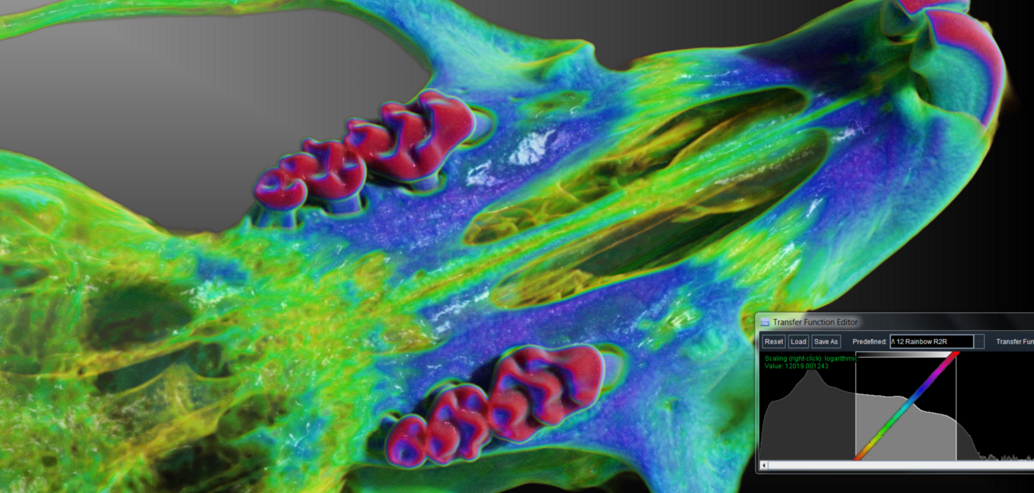
Die Einbringung des Micro-CT in das Gebäude des Translational Animal Research Center in Mainz 2020





