Graft versus Host Disease
Die allogene Transplantation von Stammzellen der Blutbildung ist eine Behandlungsmöglichkeit bei malignen hämatologischen Erkrankungen (z.B. akuten Leukämien) aber auch bei nicht malignen Erkrankungen der Hämatopoese (wie Schwere Aplastischer Anämie). Nach einer vorrausgegangenen intensiven Chemotherapie und zum Teil auch Bestrahlung wird die durch diese Therapie weitgehend zerstörte Blutbildung des Patienten (host) durch blutbildende Stammzellen eines Spenders (graft) ersetzt. Da die transplantierten Zellen die Fähigkeit zur Immunabwehr besitzen, können sie gegen das Gewebe des Empfängers reagieren und dieses schädigen. Man spricht in diesem Fall von einer „graft versus host disease“ (GvHD). Die Folgen für den Patienten können lebensbedrohend sein.
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation is a therapeutic option in malignant and non-malignant hematopoietic diseases (e.g. acute leukemia or severe aplastic anemia). By following an accepted treatment including chemo- and often radiotherapy, the hematopoietic cells of the host can be replaced by a graft of donor hematopoietic cells. Since the transplanted cells are immunocompetent, they can react with cells and tissues of the host and destroy them. This is known as graft-versus-host disease or GvHD and can be life-threatening for the patient.
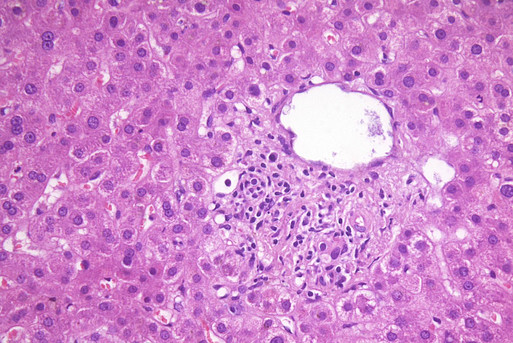
GvHD of the Liver: Lymphoid infiltration of the portal triades and small bile ducts
The allo-immunoreaction in GvHD can lead to the degeneration and death of single cells in early or low grade cases and up to the destruction of larger tissue compartments in the more advanced or severe cases. The epithelia of organs which have physiological antigen contact, i.e. the skin, gastrointestinal tract, conjunctiva and lung but also the liver are the primary targets of GvHD. A further complication is the difficulty to discern the differences between GvHD and infections or toxic drug effects which are also prevalent in patients after allogenic stem cell transplantation. This information is crucial and essential for determining strategies for subsequent therapy.
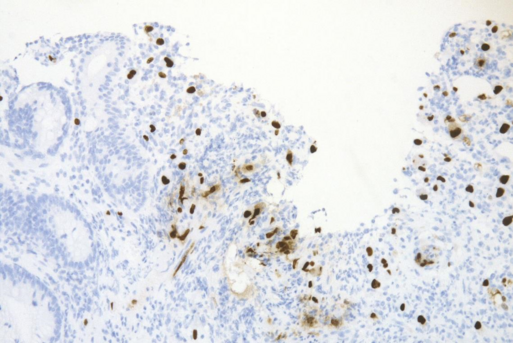
CMV-colitis in a patient after allogenec stem cell transplantation: Detection of the virus by immunohistochemistry
Projektschwerpunkte:
- Standardisierung der histologischen diagnostischen Kriterien der GvHD (standardisation of histologic diagnostic criteria in GvHD)
- Verbesserung der Interobserver Reproduzierbarkeit für Diagnose und Grading
Improving the reproducibility of the diagnosis and grading of GvHD by different evaluators - Untersuchung zur variablen Ausprägung der GvHD in unterschiedlichen anatomischen Bereichen besonders im Magen-Darm-Trakt
Investigations to evaluate the characteristics of GvHD in various anatomical regions, specifically the gastrointestinal tract. - Evaluierung der Minimalkriterien für die Diagnose der GvHD
Determine the minimal criteria for a diagnosis of GvHD
- Verbesserung der Interobserver Reproduzierbarkeit für Diagnose und Grading
- Evaluierung der Histologie als „Biomarker“ bei der GvHD in Bezug auf (evaluatehistological characteristics as a biomarker in GvHD)
- Prädiktion für ein Therapieansprechen
Histological predictors of therapy response - Prognose bezüglich des Überlebens
Prognosis of survival
- Prädiktion für ein Therapieansprechen

GvHD of the colon: Different stages and grades
Kontakt Contact:
PD Dr. Andreas Kreft andreas.kreft@unimedizin-mainz.de
Kooperationspartne Scientific partners:
Fr. Dr. Eva Wagner Drouet (3. Medizinische Klinik, Hämatologie, Universitätsmedizin Mainz)
Hr. Prof. Helmut Neumann (1. Medizinische Klinik, Endoskopie, Universitätsmedizin Mainz)
Ausgewählte Publikationen Selected References
- Diagnosis and grading of acute graft-versus-host disease in endoscopic biopsy series throughout the upper and lower intestine in patients after allogenic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a systematic approach. Kreft A, Neumann H, Schindeldecker M, Wagner-Drouet EM. Leuk Lymphoma. 2019 Jan 11:1-10. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2018.1535118. [Epub ahead of print].
- Histologic diagnosis and grading of esophageal acute graft-versus-host disease. Kreft A, Neumann H, von Bach DS, Wagner-Drouet EM. Virchows Arch. 2019 Jan 3. doi: 10.1007/s00428-018-2507-x. [Epub ahead of print].
- Dermatopathic lymphadenopathy with Langerhans cell chimerism in graft-versus-host disease of the skin. Kreft A, Krümpelmann K, Rosenwald A, Hollemann D, Wagner-Drouet EM. Eur J Haematol. 2017 Dec;99(6):582-585. doi: 10.1111/ejh.12968. Epub 2017 Oct 4.
- Consensus diagnostic histopathological criteria for acute gastrointestinal graft versus host disease improve interobserver reproducibility. Kreft A, Mottok A, Mesteri I, Cardona DM, Janin A, Kühl AA, Andrulis M, Brunner A, Shulman HM, Negri G, Tzankov A, Huber E; Gastrointestinal Pathology Group of the German-Austrian-Swiss GvHD Consortium. Virchows Arch. 2015 Sep;467(3):255-63. doi: 10.1007/s00428-015-1803-y. Epub 2015 Jul 12
- Apoptosis of ileal crypt epithelia after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation without graft-versus-host disease. Kreft A, Russo A, Lux S, Waiz L, Seidmann L, Faber J, Kirkpatrick CJ. Clin Case Rep. 2015 May;3(5):298-300. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.227. Epub 2015 Feb 19
- NIH Consensus development project on criteria for clinical trials in chronic graft-versus-host disease: II. The 2014 Pathology Working Group Report. Shulman HM, Cardona DM, Greenson JK, Hingorani S, Horn T, Huber E, Kreft A, Longerich T, Morton T, Myerson D, Prieto VG, Rosenberg A, Treister N, Washington K, Ziemer M, Pavletic SZ, Lee SJ, Flowers ME, Schultz KR, Jagasia M, Martin PJ, Vogelsang GB, Kleiner DE. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015 Apr;21(4):589-603. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2014.12.031. Epub 2015 Jan 29
- Transmission of angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma by bone marrow transplant. Kreft A, Springer E, Geissinger E, Wagner EM, Bender K, Kolbe K, Hainz M, Rosenwald A, Herr W, Kirkpatrick CJ, Meyer RG. Leuk Lymphoma. 2015 Apr;56(4):1164-7. doi: 10.3109/10428194.2014.949702. Epub 2014 Oct 9
- Mechanisms of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases in modulating T cell responses in murine graft-versus-host disease.Weber M, Lupp C, Stein P, Kreft A, Bopp T, Wehler TC, Schmitt E, Schild H, Radsak MP. PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e58110. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058110. Epub 2013 Mar 6.